In this post I will show you how to install local server on your computer.Installing a local server depends on what operating system you are using.Windows users should install WAMP,LINUX users LAMP and MAC users MAMP
Windows users follow these steps:-
Click on the downloaded file
There are only three major steps to take care of in order to get your LAMP server up and running.
Apache
From within your terminal window issue the command:
sudo apt-get install apache2
If, by chance, you are using a distribution that does not use Sudo, you will need su to the root user and issue the above command without the sudo command.
Depending on your OS installation, the above command might need to pick up some dependencies. If so, okay those dependencies. At the end of the installation, Apache should automatically start. If it doesn't, issue the following command:
sudo /etc/init.d/apache2 start
You can now open up a browser and point it to the IP address (or domain) of the server to get the famous "It works!" page. You are ready to move on to PHP.
PHP
For the purposes of this article, we will assume the "P" stands for "PHP." To begin the process of installing PHP, issue the following command:
sudo apt-get install php5 libapache2-mod-php5
NOTE: Again, depending upon your OS installation, this might require some dependencies to be met. Allow apt-get to pick up those dependencies.
When the installation is complete, restart Apache with the command:
sudo /etc/init.d/apache2 restart
Now, let's give PHP a little test to make sure it has installed. In your terminal window, create a new file called test.php.
Save that file and place it in /var/www/. Now, open up your browser to the address http://ADDRESS_OF_SERVER/test.php. Where ADDRESS_OF_SERVER is the actual address of your server. You should see "Test PHP Page" in the browser. You are now ready to move on to MySQL.
MySQL
MySQL is the database piece of the puzzle. This installation requires a few more steps than what you've just experienced. The first step is to install the server itself with the command:
sudo apt-get install mysql-server
Again, depending upon your OS installation, there might be some dependencies to be installed. After the installation is complete you need to log into the MySQL prompt and give the administrative user a password. Do this by following these steps:
Log into MySQL with the command mysql -u root -p.
As no password has been configured, you will only need to hit enter when prompted for the password.
Enter the command SET PASSWORD FOR 'root'@'localhost' = PASSWORD ('YOURPASSWORD');Where YOURPASSWORD is the password you want to use for the administrative user.
Now quit the MySQL prompt by issuing the command quit and hitting enter.
Start the MySQL server with the command sudo /etc/init.d/mysql start.
That's it. Your LAMP server is now up and running. But what about this one-command method? Simple. From your terminal window, issue the command:
sudo tasksel
This command will open a curses-based tool (see Figure 1) which allows you to select numerous software options for installation. One of those selections is a LAMP server. All you need to do is mark LAMP server for installation (scroll down with your arrow keys and then hit the space bar to select). Once you have selected LAMP server, hit the Tab key on the "button" and hit the Enter key.
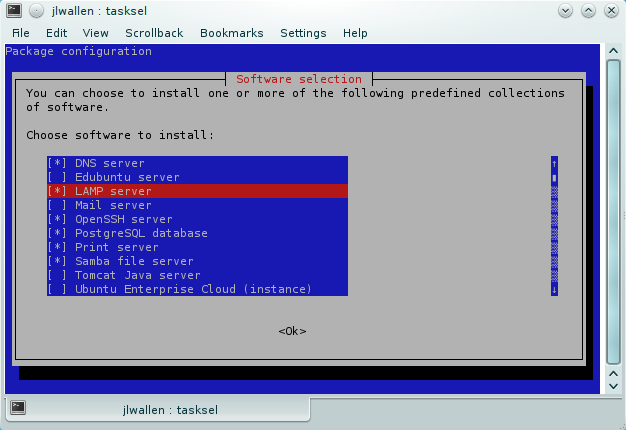
Figure 1
You will have to answer a single question when you get to the MySQL portion of the install (what you want to use for the admin password). That's it.
The Installation process is pretty simple
Windows users follow these steps:-
Click on the downloaded file
Open your favorite browser and type localhost as the url.You should get the following page which ensures your installation was successful
For Linux users:-
There are only three major steps to take care of in order to get your LAMP server up and running.
Apache
From within your terminal window issue the command:
sudo apt-get install apache2
If, by chance, you are using a distribution that does not use Sudo, you will need su to the root user and issue the above command without the sudo command.
Depending on your OS installation, the above command might need to pick up some dependencies. If so, okay those dependencies. At the end of the installation, Apache should automatically start. If it doesn't, issue the following command:
sudo /etc/init.d/apache2 start
You can now open up a browser and point it to the IP address (or domain) of the server to get the famous "It works!" page. You are ready to move on to PHP.
PHP
For the purposes of this article, we will assume the "P" stands for "PHP." To begin the process of installing PHP, issue the following command:
sudo apt-get install php5 libapache2-mod-php5
NOTE: Again, depending upon your OS installation, this might require some dependencies to be met. Allow apt-get to pick up those dependencies.
When the installation is complete, restart Apache with the command:
sudo /etc/init.d/apache2 restart
Now, let's give PHP a little test to make sure it has installed. In your terminal window, create a new file called test.php.
Save that file and place it in /var/www/. Now, open up your browser to the address http://ADDRESS_OF_SERVER/test.php. Where ADDRESS_OF_SERVER is the actual address of your server. You should see "Test PHP Page" in the browser. You are now ready to move on to MySQL.
MySQL
MySQL is the database piece of the puzzle. This installation requires a few more steps than what you've just experienced. The first step is to install the server itself with the command:
sudo apt-get install mysql-server
Again, depending upon your OS installation, there might be some dependencies to be installed. After the installation is complete you need to log into the MySQL prompt and give the administrative user a password. Do this by following these steps:
Log into MySQL with the command mysql -u root -p.
As no password has been configured, you will only need to hit enter when prompted for the password.
Enter the command SET PASSWORD FOR 'root'@'localhost' = PASSWORD ('YOURPASSWORD');Where YOURPASSWORD is the password you want to use for the administrative user.
Now quit the MySQL prompt by issuing the command quit and hitting enter.
Start the MySQL server with the command sudo /etc/init.d/mysql start.
That's it. Your LAMP server is now up and running. But what about this one-command method? Simple. From your terminal window, issue the command:
sudo tasksel
This command will open a curses-based tool (see Figure 1) which allows you to select numerous software options for installation. One of those selections is a LAMP server. All you need to do is mark LAMP server for installation (scroll down with your arrow keys and then hit the space bar to select). Once you have selected LAMP server, hit the Tab key on the "button" and hit the Enter key.

Figure 1
You will have to answer a single question when you get to the MySQL portion of the install (what you want to use for the admin password). That's it.












No comments:
Post a Comment